Introduction
In recent years, the field of molecular diagnostics has witnessed a revolution, thanks to the advent of portable DNA sequencers. Once confined to large laboratories with complex infrastructure, DNA sequencing can now be performed almost anywhere—at the bedside, in rural clinics, on a battlefield, or even in space. Portable DNA sequencers are reshaping point-of-care (POC) diagnostics by enabling rapid, accurate, and decentralized testing, with the potential to dramatically improve patient outcomes, especially in underserved areas.
Definition
Portable DNA sequencers are compact, lightweight devices designed to rapidly analyze and decode DNA sequences outside of traditional laboratory settings. They enable real-time genetic testing and data collection in the field, making DNA analysis more accessible for applications like disease detection, environmental monitoring, and forensic investigations.
The Evolution of DNA Sequencing
Traditional DNA sequencing technologies, such as Sanger sequencing and next-generation sequencing (NGS), have played critical roles in research and clinical diagnostics. However, they require expensive instruments, skilled personnel, and a controlled laboratory environment. These limitations make traditional sequencing unsuitable for urgent or remote healthcare needs.
The demand for quicker, more accessible diagnostic tools led to the development of portable DNA sequencers. Devices such as Oxford Nanopore Technologies’ MinION, Flongle, and other handheld sequencers have democratized access to genetic testing by offering a compact, user-friendly alternative that delivers results in real time.
What Makes Portable DNA Sequencers Unique?
Portable DNA sequencers differ from traditional systems in several key ways:
- Size and Portability: Weighing less than a smartphone, some portable sequencers can easily fit in a pocket or laptop bag.
- Real-Time Results: These devices allow for continuous reading of DNA strands, providing results within minutes to a few hours.
- Minimal Infrastructure Requirements: Unlike traditional sequencers, portable systems require only a laptop and internet connection, making them ideal for field use.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Intuitive software platforms help users with minimal training operate the devices efficiently.
These features make portable sequencers an excellent fit for point-of-care settings, where time, space, and resources are limited.
Applications in Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Portable DNA sequencers are being used in a wide range of point-of-care diagnostic applications, including:
Infectious Disease Detection:
Rapid detection and identification of pathogens are crucial in controlling infectious diseases. Portable DNA sequencers enable clinicians to identify bacterial, viral, and fungal infections at the source. For example, during the Ebola and Zika virus outbreaks, researchers used portable sequencers on-site to sequence viral genomes in real-time. This immediate data allowed for better tracking of outbreaks and faster decision-making.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Testing:
Antimicrobial resistance is a growing global concern. By sequencing bacterial genomes directly from clinical samples, portable devices can identify antibiotic resistance genes. This capability enables personalized treatment plans and helps prevent the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Genetic Disease Screening:
Portable sequencers are now being used to screen for genetic disorders, particularly in newborns and infants. Rapid genomic testing can help diagnose conditions such as cystic fibrosis, spinal muscular atrophy, or congenital hearing loss – allowing for timely intervention and improved quality of life.
Cancer Diagnostics:
Although more complex, some portable sequencers are capable of identifying genetic mutations associated with various cancers. Liquid biopsies—blood tests that analyze circulating tumor DNA—can be processed quickly, enabling earlier diagnosis and monitoring of treatment response.
Environmental and Zoonotic Surveillance:
Diseases that jump from animals to humans (zoonotic diseases) require close monitoring in both human and animal populations. Portable sequencers help veterinarians, field biologists, and public health workers track potential outbreaks in real-time, even in remote areas.
Benefits of Portable DNA Sequencers in POC Settings
Faster Diagnosis and Treatment:
The most significant advantage of using portable DNA sequencers at the point of care is speed. Clinicians can receive actionable data within hours, rather than waiting days for lab results. This rapid turnaround can be life-saving in critical care scenarios such as sepsis, where early and targeted treatment significantly improves survival rates.
Improved Accessibility in Remote and Low-Resource Settings:
In areas where access to central laboratories is limited, portable sequencers offer a practical solution. Healthcare workers in rural or underserved regions can perform molecular diagnostics on-site, empowering local care and reducing the need for patient transport.
Cost Efficiency:
While the initial cost of portable DNA sequencers and reagents can be high, the overall expense may be lower than traditional methods when considering transportation, infrastructure, and time savings. The ability to avoid unnecessary hospitalizations or ineffective treatments can also reduce long-term healthcare costs.
Enhanced Outbreak Response:
During infectious disease outbreaks, portable sequencers allow for immediate genomic surveillance. By identifying and tracking mutations, public health officials can adjust containment and treatment strategies in real-time.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their promise, portable DNA sequencers face several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption:
- Data Interpretation: Sequencing data can be complex. While software tools are improving, non-experts may still struggle to interpret results accurately.
- Sample Preparation Requirements: Although sequencing is rapid, preparing samples for analysis can be time-consuming and may still require laboratory equipment.
- Regulatory and Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality, regulatory approval, and clinical validation remains a hurdle, particularly for diagnostic use.
- Data Security and Privacy: Genomic data is highly sensitive. Portable systems must implement secure data handling practices to protect patient privacy.
The Future Trends of Portable DNA Sequencing Market
Rising Adoption in Point-of-Care and Field Diagnostics:
As healthcare moves toward decentralized models, the demand for portable DNA sequencers in point-of-care and remote settings is accelerating. These devices are increasingly used in clinics, rural hospitals, and field missions for rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases and genetic conditions.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Cloud Computing:
Future portable sequencers will likely incorporate AI-driven analytics for faster and more accurate data interpretation. Cloud-based platforms will also enable seamless data sharing and real-time collaboration between healthcare professionals, even in remote areas.
Expansion in Personalized Medicine:
With growing interest in personalized healthcare, portable sequencers will play a key role in on-site genomic profiling. This will enable tailored treatment decisions, especially for cancer, rare diseases, and pharmacogenomics.
Technological Advancements and Miniaturization:
Ongoing innovation is driving miniaturization, making devices more compact, cost-effective, and user-friendly. Future models may integrate sample preparation, sequencing, and analysis into a single, handheld device.
Increased Use in Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring:
Beyond healthcare, portable DNA sequencers are gaining traction in agriculture, food safety, and environmental biology. Farmers, conservationists, and researchers can use these tools for on-site detection of pathogens, GMOs, or biodiversity assessments.
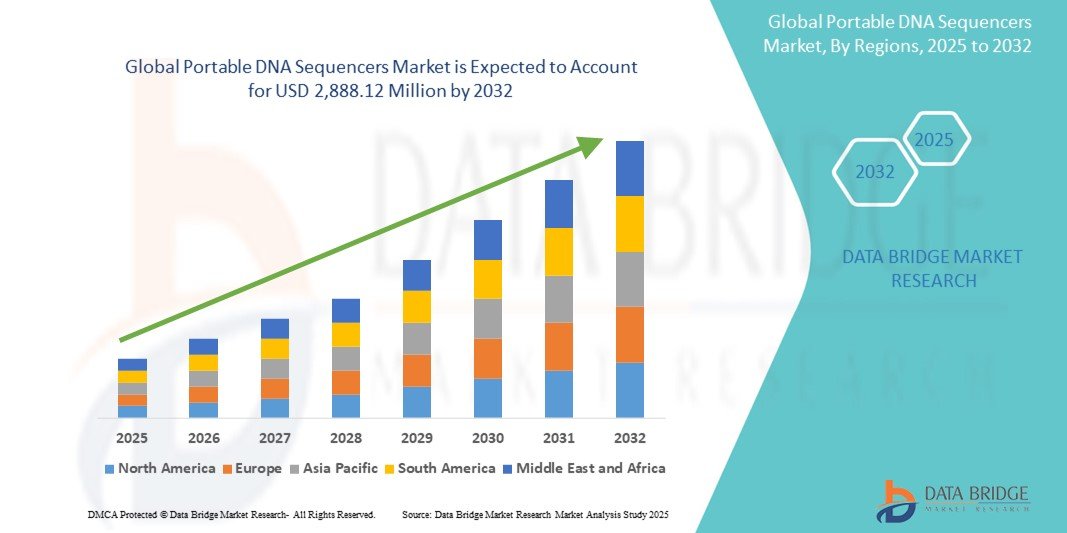
Growth Rate of Portable DNA Sequencers Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the global portable DNA sequencers market was calculated at USD 931.1 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.20% to reach USD 2,888.12 million by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-portable-dna-sequencers-market
Conclusion
Portable DNA sequencers are transforming the landscape of point-of-care diagnostics. By bringing powerful molecular analysis tools directly to the patient, these devices enable faster, more accurate diagnoses and open new possibilities for personalized and accessible healthcare. As technology advances and adoption expands, portable sequencing will play a pivotal role in reshaping global healthcare delivery, making high-quality diagnostics available to anyone, anywhere.