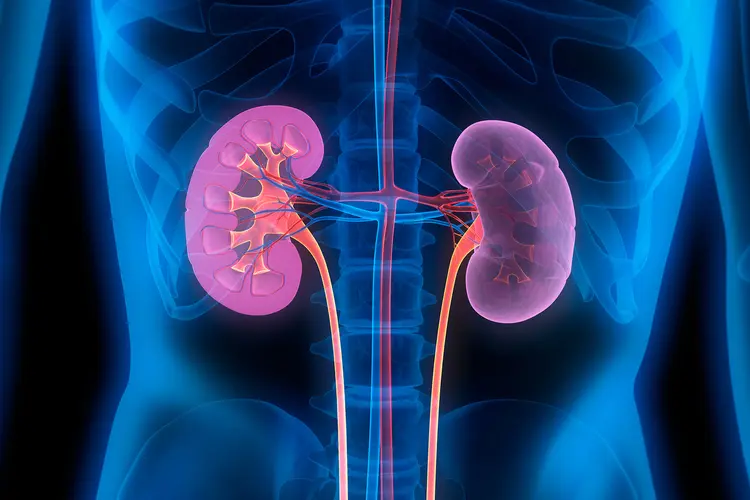
Kidney disease is a growing concern worldwide, affecting millions of individuals each year. The kidneys, two bean-shaped organs located at the back of the abdomen, are vital in filtering waste products and excess fluids from the blood. They also help regulate blood pressure, red blood cell production, and calcium balance. When these organs become damaged or diseased, it can lead to a host of serious health complications, including kidney failure. The good news is that kidney disease is often preventable with the right lifestyle choices. In this article, we’ll explore some expert tips to prevent kidney disease and maintain kidney health.
Understanding Kidney Disease
Kidney disease refers to the gradual loss of kidney function over time. It can be caused by several factors, with the most common being high blood pressure and diabetes. Both of these conditions put extra strain on the kidneys, leading to potential damage. Other risk factors include smoking, obesity, and a family history of kidney disease.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive condition, meaning it worsens over time. However, if caught early, CKD can be managed to prevent further damage. In its early stages, kidney disease often shows no symptoms, making regular screenings crucial, especially for those at higher risk.
Expert Tips for Preventing Kidney Disease
1. Control Blood Pressure
One of the most important steps you can take to prevent kidney disease is to keep your blood pressure under control. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is one of the leading causes of kidney damage. When blood pressure is consistently high, it can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste effectively.
Experts recommend that adults aim for a blood pressure reading of less than 130/80 mmHg. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and, if necessary, medication can help manage blood pressure levels. Reducing sodium intake, limiting alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight are all important lifestyle changes that can help keep blood pressure in check.
2. Manage Diabetes Effectively
If you have diabetes, it is essential to manage the condition well. High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys over time, leading to diabetic kidney disease, a common form of kidney disease. To reduce the risk, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan.
Eating a balanced diet, staying active, and taking prescribed medications can help keep blood sugar levels stable. It’s also important to track any changes in your health, such as swelling in the feet or ankles, which could indicate kidney involvement.
3. Adopt a Health and Wellness Lifestyle
Health and wellness living a healthy lifestyle is one of the most effective ways to protect your kidneys. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall kidney function. Limiting processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-sodium items is essential for kidney health.
In addition to a proper diet, staying active is crucial for maintaining kidney health. Regular physical activity helps control blood pressure, manage diabetes, and maintain a healthy weight—all factors that reduce the risk of kidney disease. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week.
Maintaining a healthy weight is another key aspect of kidney disease prevention. Obesity increases the risk of high blood pressure and diabetes, both of which contribute to kidney damage. By maintaining a healthy weight, you reduce your risk of developing conditions that can lead to kidney disease.
4. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for kidney health. Drinking enough water helps the kidneys filter waste and flush out toxins from the body. Dehydration can strain the kidneys, leading to kidney stones and other complications. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to hydration, experts suggest drinking at least eight glasses (2 liters) of water a day, depending on your individual needs and activity levels.
Be mindful of your fluid intake if you have kidney disease, as excessive water intake can sometimes worsen kidney function in certain cases. It’s best to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations on hydration.
5. Avoid Overuse of Painkillers
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain medications, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, are commonly used for managing pain, but prolonged or excessive use of these drugs can harm the kidneys. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), in particular, can cause kidney damage when taken regularly, as they reduce blood flow to the kidneys.
If you need to take pain medication, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest time possible. Always follow the instructions on the label and consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns about the impact of painkillers on your kidney health.
6. Quit Smoking
Smoking is another major risk factor for kidney disease. It damages blood vessels, reduces blood flow to the kidneys, and increases the risk of high blood pressure and diabetes. If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your kidneys—and your overall health.
Smoking cessation can improve kidney function and reduce the risk of complications associated with kidney disease. Seek support from healthcare providers, support groups, or cessation programs if you need help quitting.
7. Regular Checkups and Screenings
Regular checkups and screenings are vital for catching kidney disease early, especially if you have risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, or a family history of kidney problems. Routine blood tests can measure kidney function and detect early signs of kidney disease, even before symptoms appear.
Early detection is key to managing kidney disease and preventing it from progressing to kidney failure. If you’re at risk, talk to your healthcare provider about how often you should be screened for kidney function.
8. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the kidneys over time. Alcohol can raise blood pressure, cause dehydration, and increase the risk of kidney stones. To reduce the risk, it’s important to limit alcohol intake.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that men limit their alcohol consumption to no more than two drinks per day, and women should have no more than one drink per day. If you’re concerned about your alcohol consumption, talk to your doctor about strategies to cut back.
9. Protect Against Infections
Infections can affect the kidneys, especially urinary tract infections (UTIs) and kidney infections. UTIs can spread to the kidneys if left untreated, leading to more serious complications. To reduce the risk of infections, practice good hygiene, stay hydrated, and urinate regularly.
If you experience symptoms of a UTI, such as painful urination, frequent urination, or cloudy urine, seek medical attention promptly to prevent the infection from reaching the kidneys.
Final Thoughts
Kidney disease is a serious health concern, but with the right lifestyle changes, it is often preventable. By controlling blood pressure, managing diabetes, adopting a health and wellness-focused lifestyle, staying hydrated, avoiding overuse of painkillers, quitting smoking, and regularly checking in with your healthcare provider, you can significantly reduce your risk of kidney disease and maintain optimal kidney health.
Remember, prevention is key. Make the necessary changes to your diet, exercise routine, and overall lifestyle to ensure your kidneys stay healthy and functioning well for years to come.